About the case
- Therapeutic area: Blood diseases/Rare diseases
- Phase III
- Impact of Model Informed Drug development: Describing
Conclusion
The analyses showed that crovalimab concentrations above approximately 100 μg/mL resulted in inhibition of terminal complement activity as indicated by low values of terminal complement activity as a pharmacodynamic (PD) efficacy marker (Figure 1). The predicted drug trough concentration at steady state remained above the threshold of 100 µg/mL in >95% of simulated patients (Figure 2).
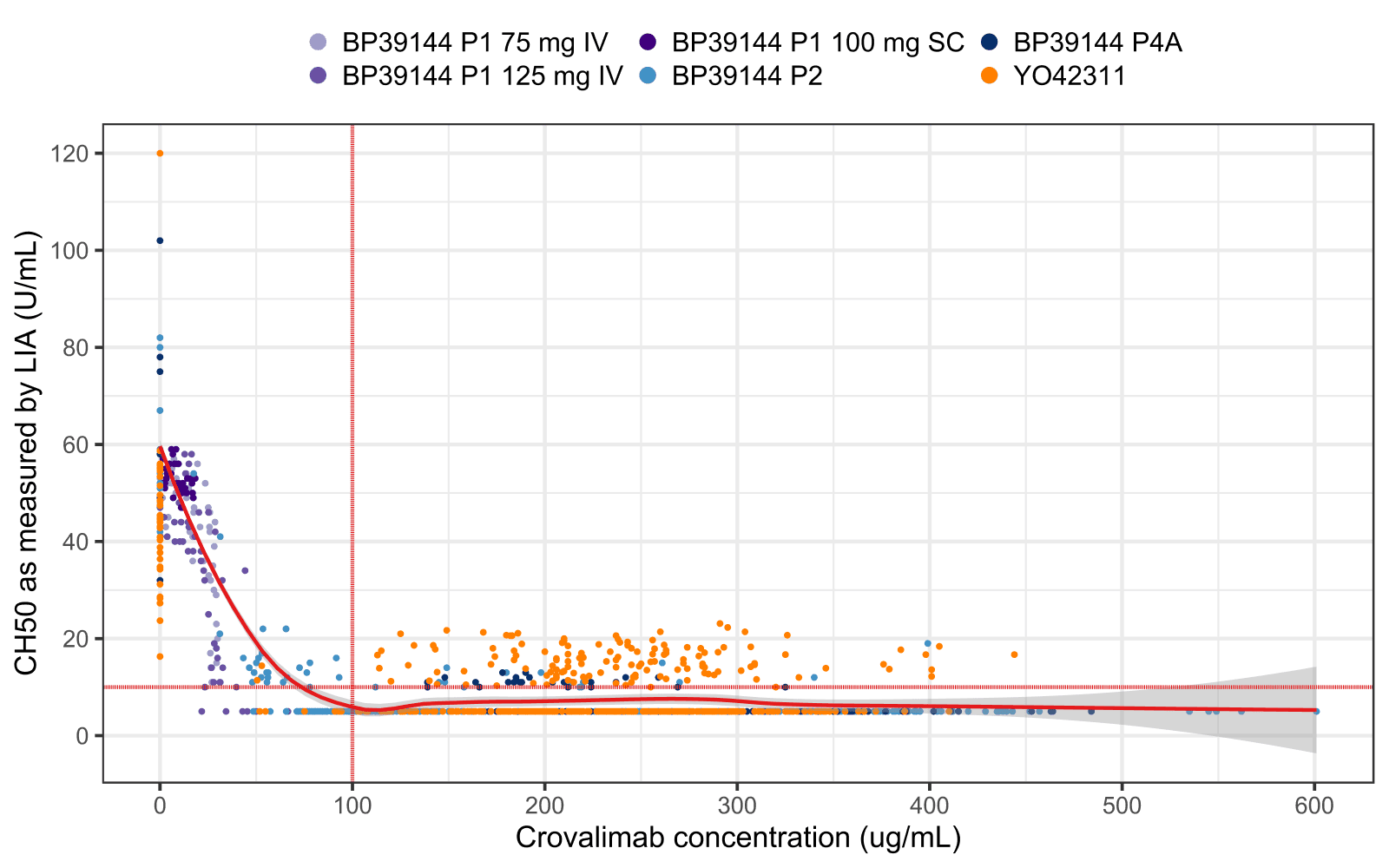
Figure 1. Graphical analysis of terminal complement activity (50% hemolytic activity [CH50] as measured by liposome immunoassay show good at efficacy at crovalimab exposure above 100 µg/mL.
- Main challenges were short timelines and several pre-defined subgroup (covariate) analyses to perform.
- Pharmetheus infrastructure, with scripted reports directly connected to the data and analysis results, enabled a fast turnaround of the regulatory submission ready report within only a few weeks after data base lock, assisting the client with dose justification and reporting of PK, PK/PD and exposure-response (efficacy/safety) analyses.
- Methodologically, a model-based population PK analysis, with evaluation of potential covariates and graphical exposure-response analysis of terminal complement activity (50% hemolytic activity [CH50] as measured by liposome immunoassay) were performed.
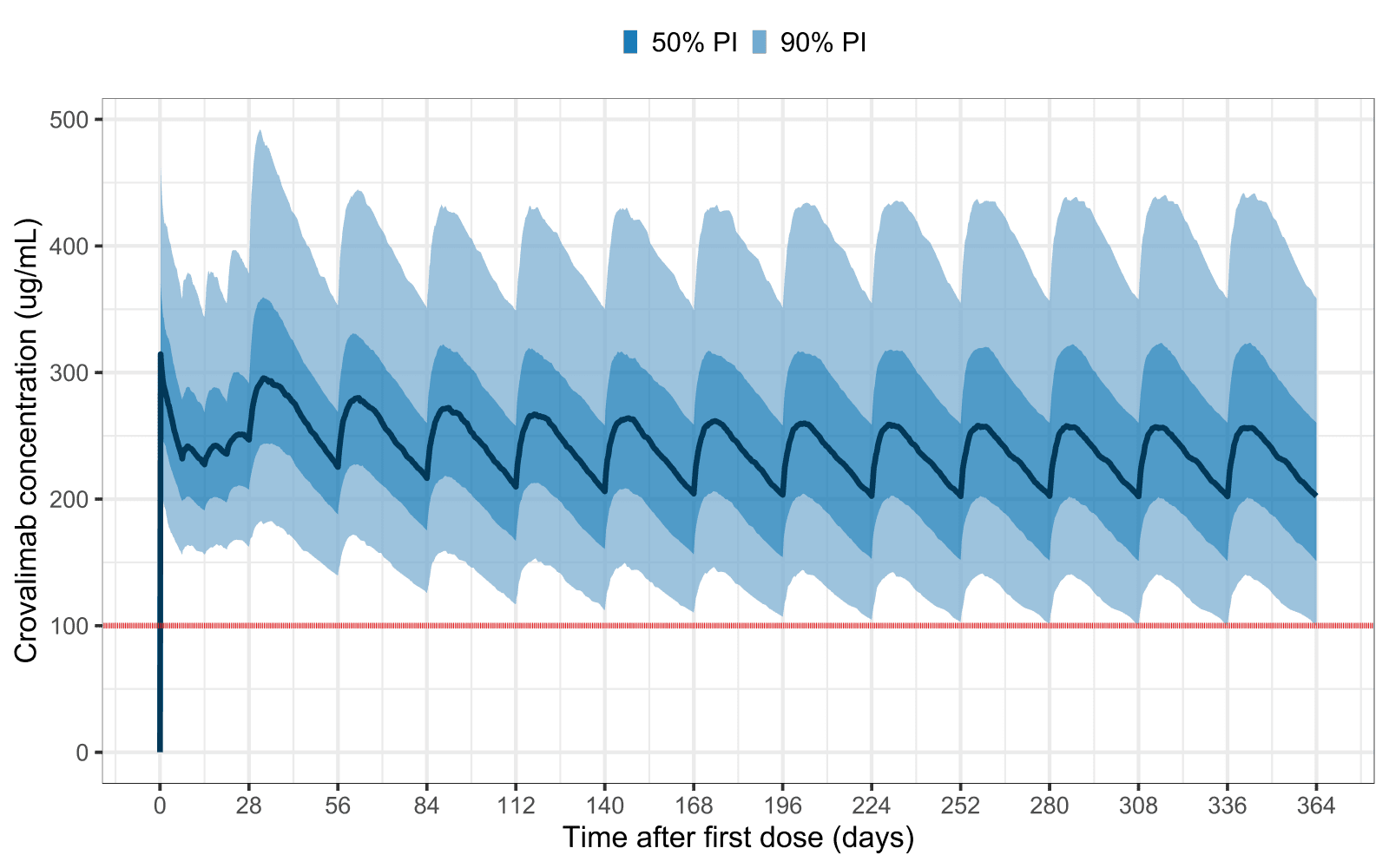
Figure 2. >95% of a representative study population achieved crovalimab trough exposure ≥ 100 µg/mL